Creating a safe and healthy work environment is not only crucial for the well-being of employees but also for the success of any organization. Industrial hygiene, also known as occupational hygiene, is a field that focuses on identifying, assessing, and controlling workplace hazards to protect the health and well-being of workers.
The primary goal of industrial hygiene is to prevent work-related illnesses, injuries, and adverse health effects by implementing control measures and promoting safe work practices. Industrial hygienists employ a combination of qualitative and quantitative assessments to evaluate and manage a wide range of workplace hazards, including chemical, physical, biological, and ergonomic factors.
Here are some key aspects of industrial hygiene:
1. Hazard Identification: Industrial hygienists systematically identify potential workplace hazards by conducting thorough inspections, surveys, and evaluations. They analyze various factors such as exposure levels, concentration of harmful substances, noise levels, lighting conditions, and ergonomic design.
2. Risk Assessment: Industrial hygienists assess the risk associated with identified hazards, considering factors like exposure duration, frequency, and intensity. They evaluate the potential health effects on workers, determine acceptable exposure limits, and prioritize interventions based on the severity of risks.
3. Exposure Monitoring: This involves measuring and quantifying workers’ exposure to hazardous substances or physical agents. Industrial hygienists use monitoring equipment to collect air samples, noise data, vibration levels, and other relevant measurements. These measurements help determine compliance with exposure standards and identify areas for improvement.
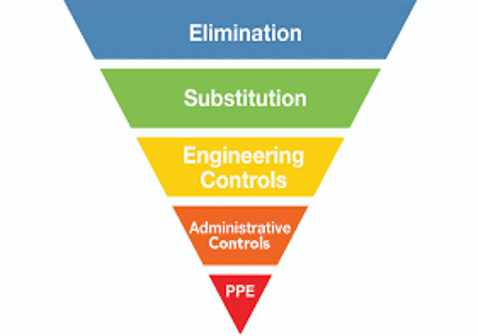
5. Training and Education: Industrial hygienists play a crucial role in educating workers and management about occupational hazards, safe work practices, and the proper use of protective measures. They provide training programs, guidelines, and resources to promote a culture of safety and awareness in the workplace.
6. Regulatory Compliance: Industrial hygienists stay informed about relevant regulations and standards set by governmental agencies such as the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety in Canada. They ensure that employers adhere to these regulations and assist in developing compliance strategies.
A Quest for Safer, Healthier Work Environments
Industrial hygiene stands as a vital pillar in our quest for safer, healthier work environments. The dedicated efforts of industrial hygienists help shape workplaces that prioritize the well-being of employees, leading to increased productivity, reduced incidents, and a positive organizational culture.
Overall, industrial hygiene aims to create safe and healthy work environments, prevent work-related illnesses and injuries, and improve the well-being of employees through the identification, assessment, and control of occupational hazards.
Reach Out to Our Team!
How Can We Help You?
Contact us at JADA Solutions (HSE) Inc. to speak with one of our professionals!
Newsletter
📹 Watch our latest Safety Toolbox Talk: Mould and Fungi 101: Viable vs. Non-Viable Mould Testing
💡Are all moulds considered fungi? And why should we care? This leads us to explaining the two different types of testing for mould exposure: viable vs non-viable.
🔍 Lead and Heavy Metal Exposure: Are You Protecting Your Workers?
Lead and other heavy metals can quietly put your team at serious risk - especially during construction, demolition, or manufacturing projects.
Our last Asbestos Worker in Alberta 2-Day Training Course before the Summer season happens at the end of this month!
🗓️ June 24th - 25th
⏰ 8AM - 5PM
💵 $525
📍 Sherwood Park, AB
Claim your spot now! 👉


